For years, the Internet of Things (IoT) conversation has been dominated by sensors, cloud platforms, and the flashier world of AI analytics. While AI remains the current “buzzword,” the reality is that millions of IoT devices are already quietly working in the background, providing the essential sensor data that powers our modern world. However, as these deployments mature and scale, a critical bottleneck has emerged: the cost and physical limits of data transmission.
In my experience with Air Quality Monitoring (AQM) solutions, I’ve seen this play out repeatedly. Projects often aim to transmit high-frequency, continuous air quality measurements over long distances, only to hit a wall. Whether it’s the strict payload size limits of LoRaWAN or the spiraling costs of high-frequency transmissions over LTE/NB-IoT, the “raw data” approach is no longer sustainable.
The Problem with “Raw” Transmission
Most IoT data, especially from air quality sensors, is highly structured and repetitive. Devices often transmit variations of the same environmental measurements over and over. Sending this information raw ignores a simple reality: transmission is expensive, not just in terms of data plans, but in battery life, maintenance, and long-term operational costs.
As the industry matures, we are seeing a shift in mindset. Compression is no longer just a low-level technical detail; it is becoming a foundational technology because it makes large-scale deployments sustainable.
Three Pillars of IoT Compression
Integrating lossless compression directly onto the device, rather than relying on the cloud, transforms it into a perpetual efficiency engine. This creates several vital second-order effects:
- System Resilience: Fewer transmissions lead to less network congestion and fewer collision points. This reduces “chatter” and makes systems like city-wide AQM grids significantly more reliable.
- Extended Battery Life: Radio transmissions are the primary power drain for most IoT devices. By reducing how often a device needs to “speak,” we can extend battery life dramatically, reducing the need for expensive “truck rolls” to replace batteries in the field.
- Enhanced Data Quality: Paradoxically, compression allows you to collect more data. By transmitting more intelligently, devices can sample at higher frequencies to capture micro-events and short-lived anomalies that would otherwise be lost due to bandwidth constraints.
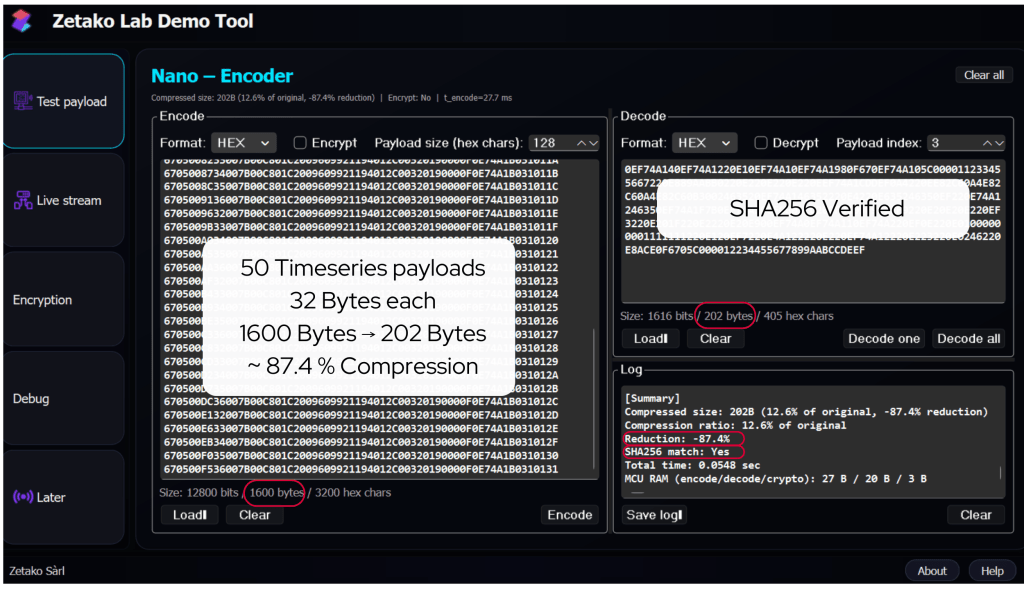
Real-World Efficiency: The Up-to 87% Reduction
The potential for this technology is best illustrated by modern encoders capable of high-ratio reduction. For instance, testing with 50 timeseries payloads (32 bytes each) shows a raw size of 1600 bytes being compressed down to just 202 bytes—an 87.4% reduction (Source: Zetako Lab Demo Tool). This level of efficiency allows for high-granularity monitoring even on restricted protocols like LoRaWAN.
| Metric | Raw Data | Compressed Data |
| Payload Size | 1600 Bytes | 202 Bytes |
| Reduction | 0% | 87.4% |
| Integrity | N/A | SHA256 Verified |
Conclusion
The future of IoT won’t be defined by who collects the most raw data, but by who uses fewer resources to learn more. In critical infrastructure like healthcare, transportation, and air quality monitoring, these efficiency choices compound.
Compression is no longer just a “feature”, it is a lifeline. Without it, IoT cannot scale sustainably to meet the demands of our data-driven future.